I. Project objective
The objective of the project is to develop a modern and innovative energy complex based on renewable energy sources (RES), hydrogen technologies, and large-scale underground energy storage in salt caverns. The complex will be integrated with Poland’s national electricity system and will include the capability to export hydrogen and energy to Germany and other EU markets.
II. Formal and investment status and locations
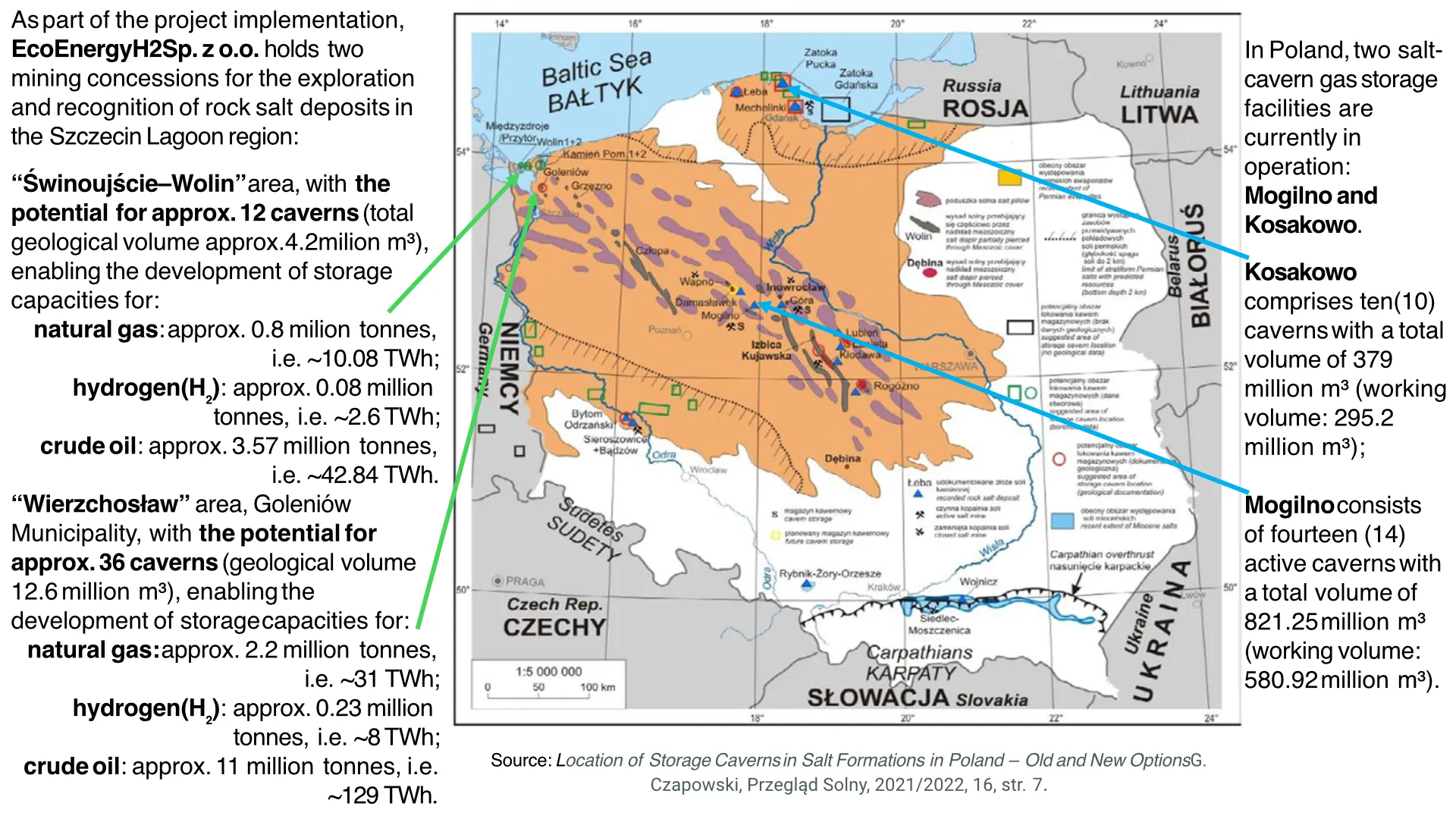
The company holds two concessions for the exploration and recognition of rock salt deposits:
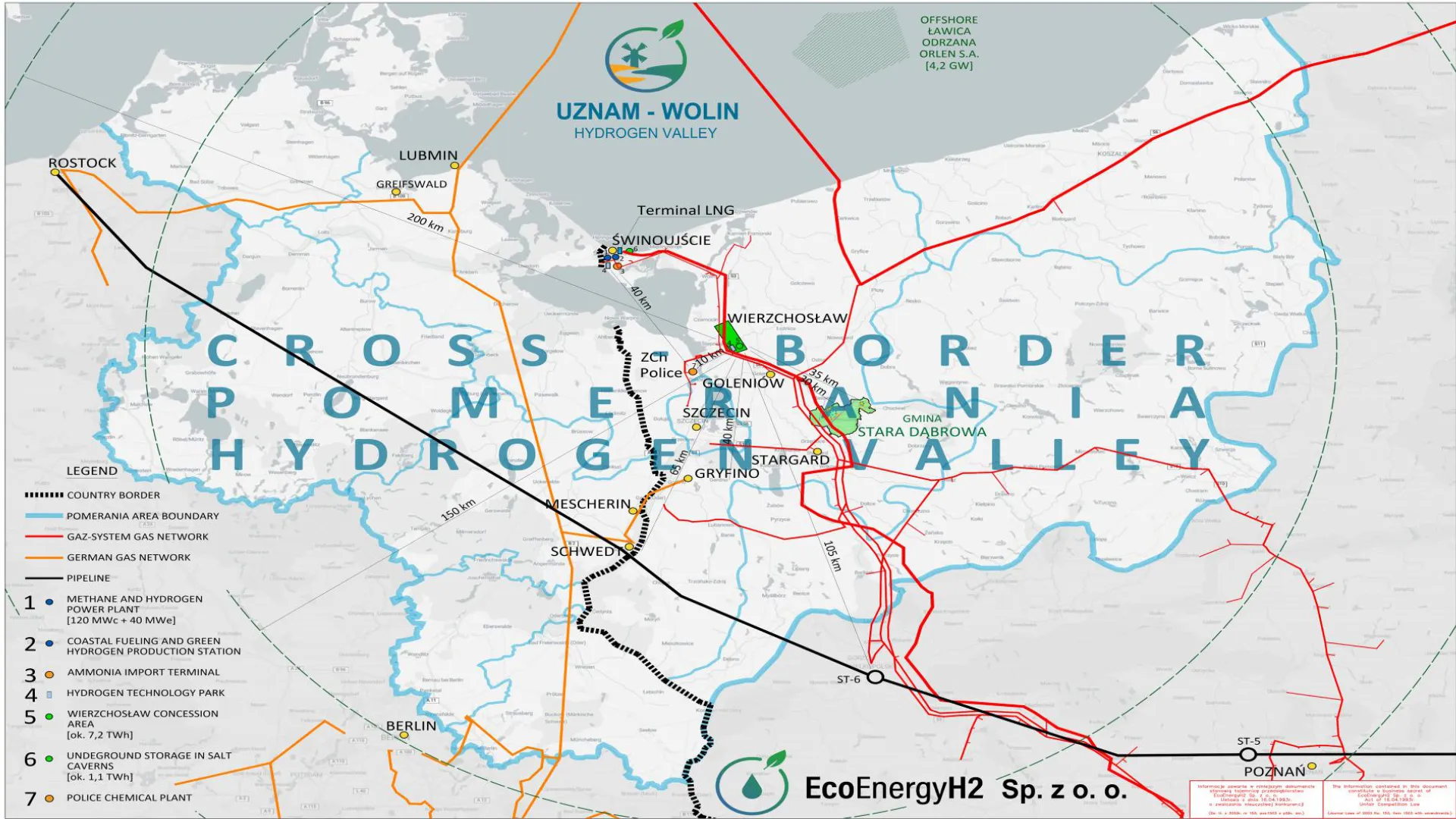
- Location 1 – Wolin Island “Świnoujście–Wolin” area, Świnoujście Municipality, West Pomeranian Voivodeship
- Location 2 – Southern Szczecin Lagoon Region “Wierzchosław” area, Goleniów, Stepnica and Przybiernów Municipalities, West Pomeranian Voivodeship
Both concessions authorize geological works and allow the creation of salt caverns for large-scale energy storage.
Ministry map showing the company's concessions
III. Key Elements of the Project
1/ Energy Storage Potential in Salt Caverns
The caverns will serve as large-scale storage facilities for: hydrogen, natural gas, crude oil and CO₂.
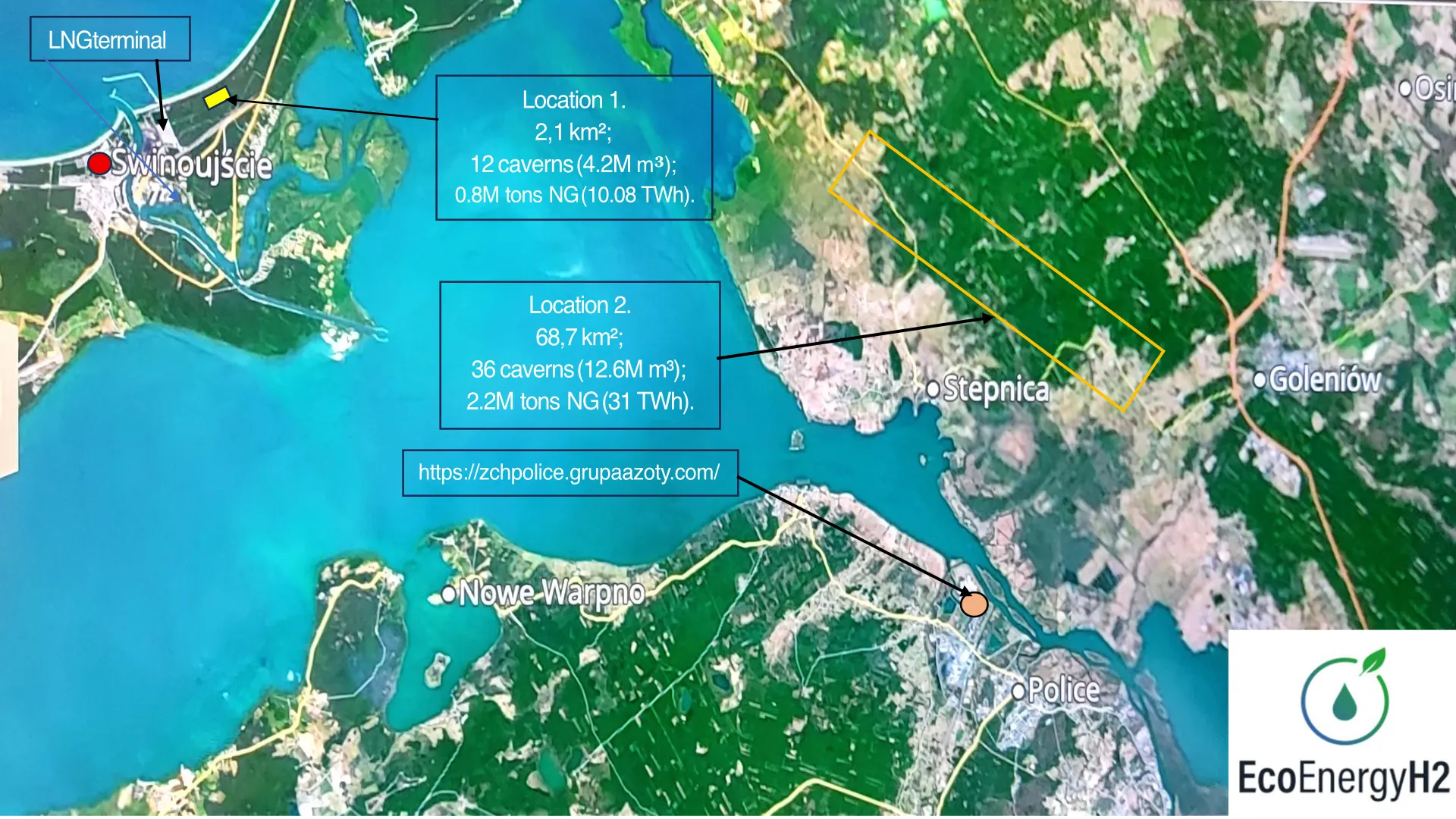
Location 1 – Świnoujście / Wolin Island
Planned: up to 12 caverns with the following total storage capacities:
- Hydrogen: approx. 0.08 Mt (864 million Nm³; 2.64 TWh)
- Natural gas: approx. 0.73 Mt (970 million Nm³; 10.08 TWh)
- Crude oil: approx. 3.57 Mt (4.2 million Nm³; 42.84 TWh)
Strategic advantages:
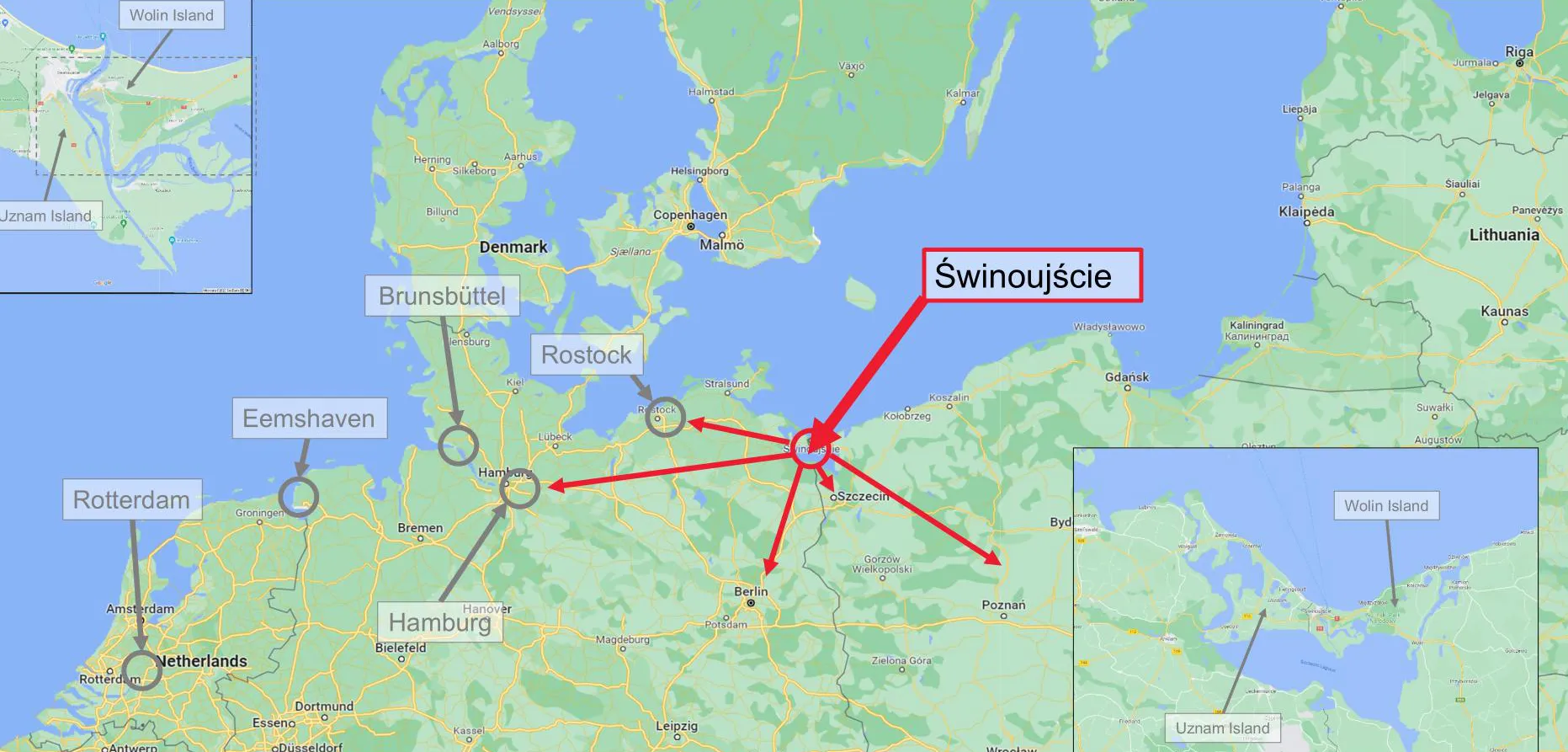
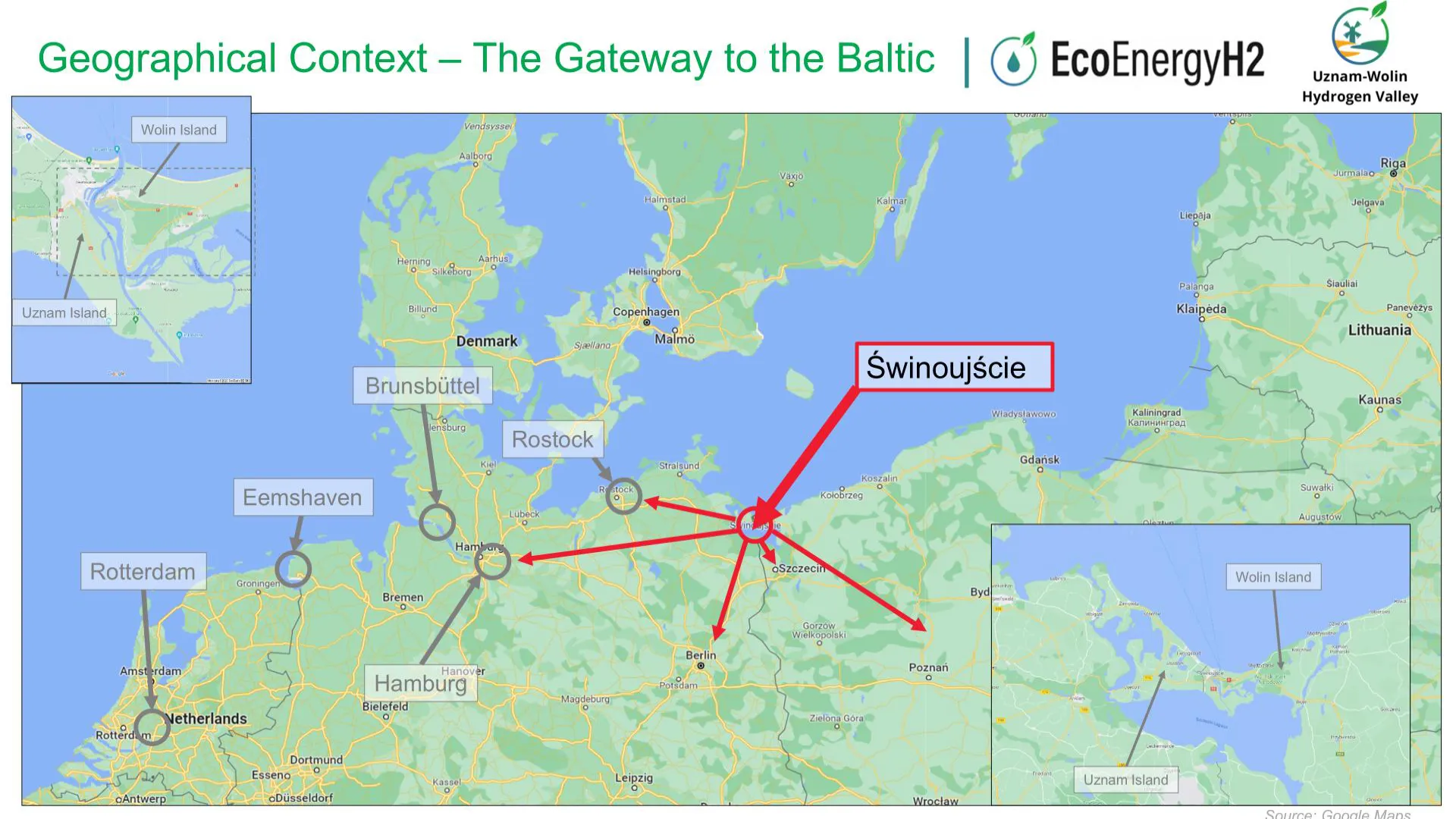
- close proximity to the LNG terminal and Gaz-System transmission network,
- integration potential with the planned deep-water container terminal,
- ability to use pressure differentials in cavern operation for green electricity generation via expanders,
- capability to stabilize RES production and supply port infrastructure.
Location 2 – Szczecin Lagoon Region
- Planned: up to 36 caverns with the following total storage capacities:
- Hydrogen: approx. 0.23 Mt (1,440.49 million Nm³; 7.92 TWh)
- Natural gas: approx. 2.19 Mt (2,908.72 million Nm³; 30.24 TWh)
- Crude oil: approx. 10.71 Mt (12.8 million Nm³; 128.52 TWh)
2/ Production and System-Balancing Potential
- Hydrogen production: up to 200 tonnes/day (~440 MW of alkaline electrolyzers)
- Electricity system balancing: up to 5 GW and 44 TWh
- Integration with:
- offshore wind farms,
- new PSE transmission infrastructure,
- Gaz-System pipeline network,
- the “Friendship” crude oil pipeline (PERN).
3/ Alignment with Strategic National Documents
- EEH2 project included in the PSE Development Plan 2025–2034.
- Submitted to the Hydrogen Map of Poland (GAZ-SYSTEM).
- Local institutional support confirmed through the establishment of the Usedom–Wolin Hydrogen Valley Association.
4/ Cross-Border Dimension and Energy Security
- Potential hydrogen transmission towards Germany through the Oder Corridor.
- Caverns may serve as strategic reserves of natural gas and crude oil for Poland and eastern Germany.
- The project enhances energy security and resilience for the region and the EU.
5/ Key Infrastructure Connections
The planned storage facilities are located close to:
- approx. 100 km from the final Polish compressor station of the “Friendship” pipeline (linking to PCK Schwedt refinery and Rostock port),
- approx. 10 km from Grupa Azoty Police,
- approx. 40 km from Gryfino,
- approx. 70 km from PCK Schwedt refinery (Germany) and planned cross-border hydrogen and oil corridors connecting Poland, Germany and the EU.